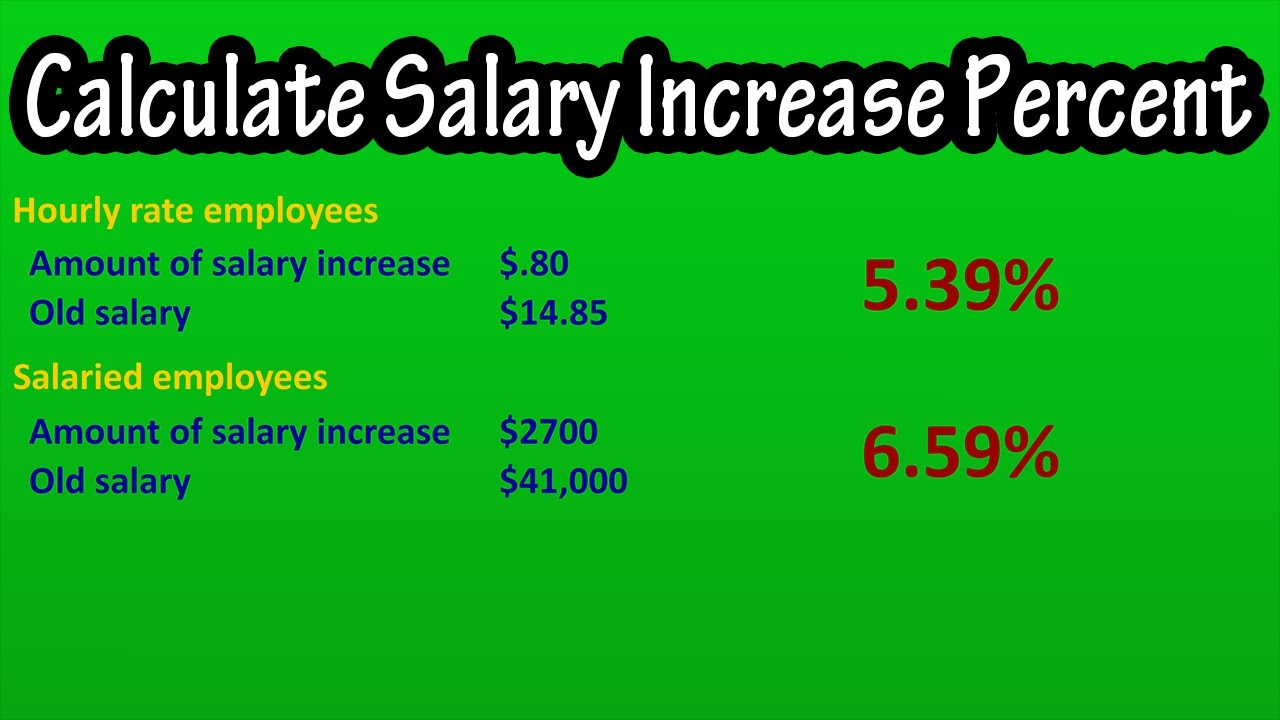
A salary increase, or pay raise, is an adjustment to an employee’s compensation. It’s often given to reward performance, recognize increased responsibilities, or adjust for inflation.
Calculating a Salary Increase
1. Determine the Raise Percentage:
- This percentage is often decided based on factors like performance reviews, company budget, and market rates.
2. Calculate the Raise Amount:
- Multiply the current salary by the raise percentage (in decimal form).
- For example, for a 5% raise on a $50,000 salary:
- Raise amount = $50,000 * 0.05 = $2,500
3. Calculate the New Salary:
- Add the raise amount to the current salary.
- New salary = $50,000 + $2,500 = $52,500
Factors Affecting Salary Increases
- Performance: Outstanding performance is often rewarded with higher pay raises.
- Experience and Skills: Increased experience and skills can lead to higher salaries.
- Market Rates: Companies often adjust salaries to stay competitive with industry standards.
- Company Performance: The financial health of the company can impact the availability of funds for pay raises.
- Economic Conditions: Inflation and economic growth can influence salary increases.
- Negotiation Skills: Effective negotiation can help secure higher pay raises.
Common Salary Increase Scenarios
- Merit-Based Raises: Rewards individual performance and contributions.
- Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLAs): Adjusts salaries to account for inflation.
- Promotion-Based Raises: Increases salary when an employee is promoted to a higher-level position.
- Across-the-Board Raises: Equal pay increases for all employees, regardless of performance.
By understanding the factors that influence salary increases and using the calculation methods, you can better assess your potential earnings and negotiate for fair compensation.
Would you like more information on a specific aspect of salary increases, such as negotiating a raise or understanding the impact of inflation on salaries?