A salary structure is a framework that outlines the pay scales and compensation policies within an organization. It defines how salaries are determined, how they are distributed among different job roles, and how they are adjusted over time.
Key Components of a Salary Structure
- Job Evaluation:
- This process involves assessing the relative worth of different jobs within an organization.
- Factors considered include job responsibilities, required skills, and the level of authority.
- Job evaluation helps determine the appropriate salary range for each position.
- Pay Grades:
- Pay grades are groupings of jobs with similar levels of responsibility and skill requirements.
- Each pay grade has a specific salary range, which defines the minimum and maximum salary for jobs within that grade.
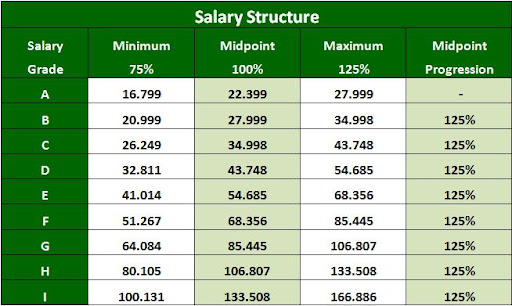
- Pay Ranges:
- A pay range is the minimum and maximum salary for a specific job or pay grade.
- It allows for flexibility in compensating employees based on factors like performance, experience, and market rates.
- Pay Scales:
- A pay scale is a graphical representation of pay ranges for different job levels.
- It helps visualize the salary structure and identify potential salary gaps.
Types of Salary Structures
- Broadbanding:
- Combines multiple traditional pay grades into broader bands.
- Offers more flexibility in compensating employees based on performance and skills.
- Can reduce bureaucratic overhead and promote career progression.
- Skill-Based Pay:
- Rewards employees based on their skills and knowledge, rather than their job title or tenure.
- Encourages continuous learning and skill development.
- Can be more complex to implement and manage.
- Competency-Based Pay:
- Relies on the employee’s ability to demonstrate specific competencies or behaviors.
- Promotes a performance-oriented culture.
- Can be challenging to measure and quantify competencies.
Factors Affecting Salary Structures
- Market Rates: External factors like industry standards and economic conditions.
- Cost of Living: The cost of living in different geographic locations.
- Company’s Financial Performance: The company’s profitability and budget constraints.
- Employee Performance and Potential: Individual performance and future potential.
- Union Contracts: Collective bargaining agreements with unions.
- Government Regulations: Minimum wage laws and other labor regulations.
By understanding the components and types of salary structures, organizations can develop effective compensation strategies that attract, motivate, and retain top talent.
Would you like to know more about a specific aspect of salary structures, such as job evaluation or pay scales?